Introduction
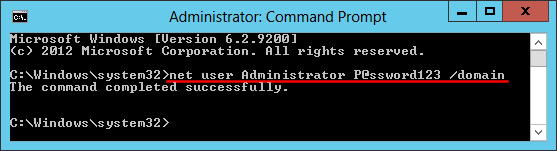
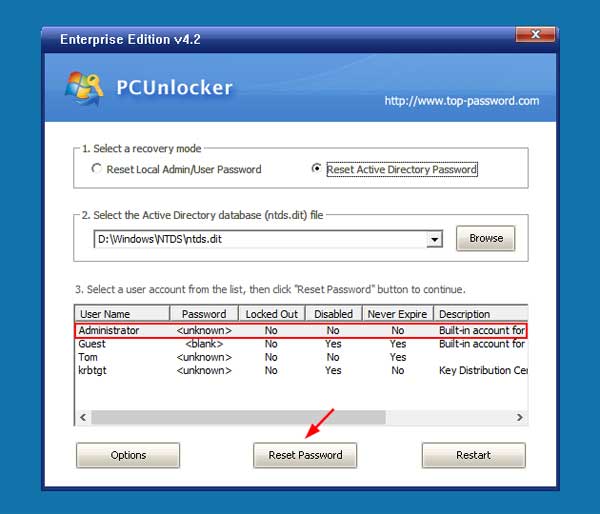
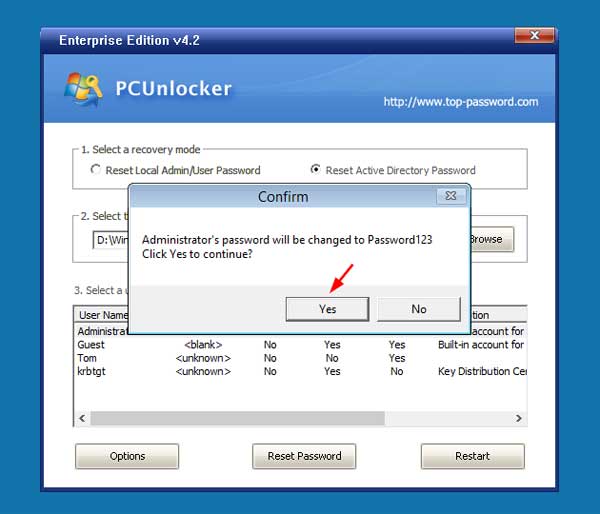
Change Local Administrator Password On Domain Controller is a process that allows you to change the local administrator password on a domain controller. This process is important for maintaining the security of your domain controller and ensuring that only authorized users have access to the system. This guide will provide step-by-step instructions on how to change the local administrator password on a domain controller
How to Change the Local Administrator Password on a Domain Controller
Changing the local administrator password on a domain controller is an important security measure that should be done regularly. This article will provide a step-by-step guide on how to change the local administrator password on a domain controller.
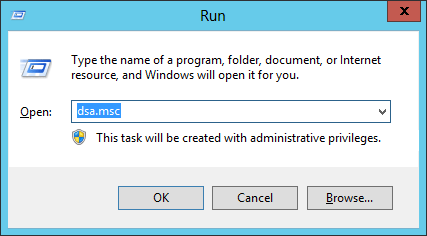
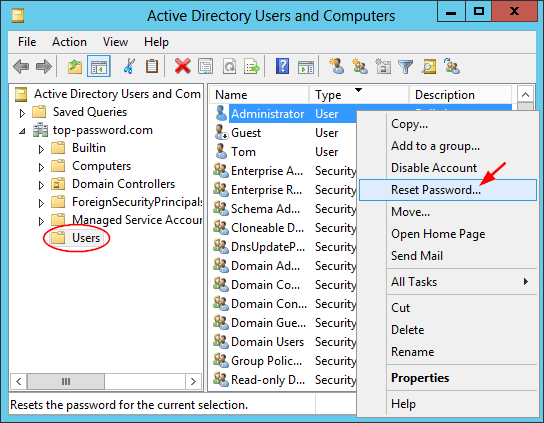
1. Log in to the domain controller with an account that has administrative privileges.
2. Open the Control Panel and select “User Accounts”.
3. Select “Manage User Accounts”.
4. Select the “Local Users and Groups” option.
5. Select the “Administrators” group.
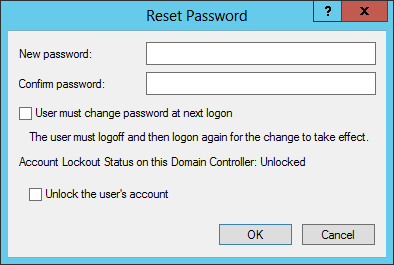
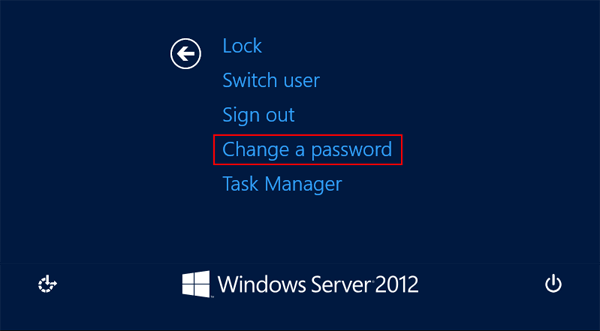
6. Select the “Change Password” option.
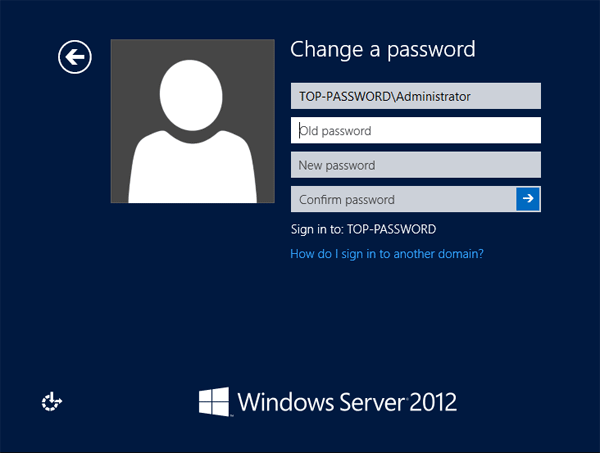
7. Enter the new password twice and click “OK”.
8. Log out of the domain controller and log back in with the new password.
It is important to note that changing the local administrator password on a domain controller will not affect any other user accounts on the domain. It is also important to ensure that the new password is secure and not easily guessed.
By following these steps, you can easily change the local administrator password on a domain controller. Doing so will help to ensure the security of your domain controller and the data stored on it.
Best Practices for Changing the Local Administrator Password on a Domain Controller
When it comes to changing the local administrator password on a domain controller, there are certain best practices that should be followed. These best practices are designed to ensure the security of the domain controller and the data it contains.
First, it is important to create a strong password. The password should be at least eight characters long and contain a combination of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and symbols. It should also be changed regularly, at least every 90 days.
Second, the password should be stored securely. It should not be written down or stored in an unsecured location. It should also not be shared with anyone who does not need access to the domain controller.
Third, the password should be changed in a secure manner. This means that the password should be changed on the domain controller itself, rather than remotely. This will help to ensure that the password is not intercepted during the change process.
Finally, it is important to keep a record of the password changes. This will help to ensure that the password is changed regularly and that any unauthorized access attempts are detected quickly.
By following these best practices, organizations can ensure that their domain controllers remain secure and that their data is protected.
The Benefits of Changing the Local Administrator Password on a Domain Controller
Changing the local administrator password on a domain controller is an important security measure that should be taken to protect the network from malicious actors. By changing the local administrator password, organizations can ensure that only authorized personnel have access to the domain controller and its resources. This can help to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems, as well as reduce the risk of malicious actors gaining access to the domain controller.
The primary benefit of changing the local administrator password on a domain controller is improved security. By changing the password regularly, organizations can ensure that only authorized personnel have access to the domain controller and its resources. This can help to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and systems, as well as reduce the risk of malicious actors gaining access to the domain controller. Additionally, changing the local administrator password can help to protect against brute force attacks, which are attempts to guess the password by trying different combinations of characters.
Another benefit of changing the local administrator password on a domain controller is improved system performance. By regularly changing the password, organizations can ensure that the domain controller is running optimally. This can help to reduce the risk of system crashes and other performance issues, which can be costly and time-consuming to fix.
Finally, changing the local administrator password on a domain controller can help to ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards. Many organizations are required to adhere to certain security standards, such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS). By regularly changing the local administrator password, organizations can ensure that they are meeting these standards and regulations.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xq9dDFIqBe0
In conclusion, changing the local administrator password on a domain controller is an important security measure that should be taken to protect the network from malicious actors. By regularly changing the password, organizations can ensure that only authorized personnel have access to the domain controller and its resources, improve system performance, and ensure compliance with industry regulations and standards.
How to Automate the Process of Changing the Local Administrator Password on a Domain Controller
Changing the local administrator password on a domain controller is an important security measure that should be done regularly. Automating this process can help ensure that the password is changed on a regular basis and that it is done in a secure manner. This article will provide a step-by-step guide on how to automate the process of changing the local administrator password on a domain controller.
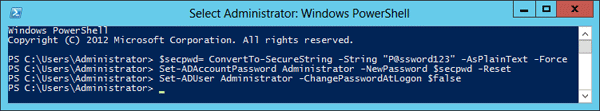
Step 1: Create a Password Reset Script
The first step is to create a password reset script. This script should be written in a scripting language such as PowerShell or VBScript. The script should include the command to reset the local administrator password, as well as any other commands necessary to ensure that the password is changed securely.
Step 2: Create a Scheduled Task
Once the script has been created, the next step is to create a scheduled task. This task should be set to run at a regular interval, such as once a week or once a month. The task should be configured to run the password reset script that was created in step one.
Step 3: Test the Script
Before the scheduled task is enabled, it is important to test the script to ensure that it works as expected. This can be done by running the script manually and verifying that the local administrator password is changed correctly.
Step 4: Enable the Scheduled Task
Once the script has been tested and verified to work correctly, the scheduled task can be enabled. This will ensure that the local administrator password is changed on a regular basis.
By following these steps, it is possible to automate the process of changing the local administrator password on a domain controller. This can help ensure that the password is changed regularly and in a secure manner.
1. Utilize a Robust Password
The foundation of security begins with a strong password. Avoid common pitfalls by crafting a password that’s complex and difficult to crack. Incorporate a mix of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special characters to fortify its strength. Remember, the more intricate the password, the harder it is for malicious actors to penetrate your defenses.
2. Safeguard in a Secure Vault
Once you’ve concocted a formidable password, the next step is to safeguard it in a secure repository. Employ trusted tools like password managers or encrypted files to store the local administrator password. These solutions offer layers of encryption and authentication, thwarting any nefarious attempts to pilfer your sensitive credentials.
3. Embrace Regular Password Rotations
Continual vigilance is key in the realm of cybersecurity. Institute a practice of regularly changing the local administrator password. By rotating passwords at predetermined intervals, you minimize the window of vulnerability and keep potential threats at bay.
4. Implement Two-Factor Authentication
Enhance your security posture by implementing two-factor authentication (2FA). This adds an extra layer of defense by requiring users to provide a secondary form of verification, such as a code sent to their mobile device or email address. By coupling this with the local administrator password, you create a formidable barrier against unauthorized access.
5. Monitor and Control Access
Maintaining oversight of who can access the local administrator password is paramount. Implement stringent access controls to ensure that only authorized personnel have the privilege to retrieve or modify the password. Regularly audit access logs to detect any anomalous activity and swiftly respond to potential security breaches.
Troubleshooting Common Password Change Issues
While changing the local administrator password is a routine security practice, it can sometimes encounter hiccups along the way. Here’s a rundown of common issues that may arise and how to troubleshoot them effectively:
Issue 1: Password Complexity Requirements Not Met
Sometimes, the domain controller may reject the new password if it fails to meet the complexity requirements. Ensure that your password includes a mix of characters and meets the minimum length criteria (typically 8 characters or more).
Issue 2: Password Recognition Failure
If the domain controller fails to recognize the new password, double-check that it’s entered correctly and synchronized across all relevant systems. This ensures seamless authentication and prevents any discrepancies that could impede access.
Issue 3: Authentication Server Unreachable
In cases where the domain controller struggles to authenticate the new password, verify that it’s correctly inputted and that the authentication server is accessible. Address any network connectivity issues promptly to restore seamless authentication processes.
Issue 4: Permissions and Resource Constraints
When the domain controller encounters difficulties applying the new password, review its permissions and ensure it has unfettered access to the necessary resources. Rectifying any permission discrepancies or resource constraints will facilitate a smooth password update process.
By proactively addressing these common issues and implementing robust security measures, you can fortify your domain controller against potential threats and ensure smooth operations within your network infrastructure. Remember, in the realm of cybersecurity, prevention is always preferable to remediation. Stay vigilant, stay secure!
- [SOLVED] reset admin password – Windows Server
- Active Directory: How to Change the Local Administrator Password …
- Windows Server 2016 Standard | Any way to change Local Admin …