Introduction
This guide will provide an overview of how to use the Change Local Administrator Password Group Policy in Server 2016. This policy allows administrators to set a password for the local administrator account on all computers in the domain. This policy is useful for ensuring that all computers in the domain have the same local administrator password, making it easier to manage and secure the network. Additionally, this policy can be used to ensure that the local administrator password is changed on a regular basis, making it more difficult for malicious actors to gain access to the network.
How to Change Local Administrator Password Group Policy in Server 2016
Changing the local administrator password in Server 2016 using Group Policy is a straightforward process. This article will provide a step-by-step guide on how to do so.
Step 1: Open the Group Policy Management Console.
To open the Group Policy Management Console, open the Run dialog box by pressing the Windows key + R. Type “gpmc.msc” and press Enter.
Step 2: Create a new Group Policy Object (GPO).
Right-click on the domain name in the left pane and select “Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…” Give the GPO a name and click OK.
Step 3: Edit the GPO.
Right-click on the newly created GPO and select “Edit…”.
Step 4: Navigate to the Security Settings.
In the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options.
Step 5: Configure the Password Policy.
In the right pane, double-click on “Accounts: Rename administrator account” and select “Enabled”. Enter the new name for the local administrator account and click OK.
Step 6: Configure the Password Expiration Policy.
In the right pane, double-click on “Accounts: Maximum password age” and select “Enabled”. Enter the number of days after which the password should expire and click OK.
Step 7: Configure the Password Complexity Policy.
In the right pane, double-click on “Password must meet complexity requirements” and select “Enabled”. Click OK.
Step 8: Configure the Password History Policy.
In the right pane, double-click on “Enforce password history” and select “Enabled”. Enter the number of passwords to remember and click OK.
Step 9: Configure the Password Length Policy.
In the right pane, double-click on “Minimum password length” and select “Enabled”. Enter the minimum number of characters for the password and click OK.
Step 10: Link the GPO to the Domain.
Right-click on the domain name in the left pane and select “Link an Existing GPO…”. Select the GPO you created and click OK.
Step 11: Force the GPO to Apply.
Open the Command Prompt as an administrator and type “gpupdate /force”. This will force the GPO to apply to all computers in the domain.
By following these steps, you can easily change the local administrator password in Server 2016 using Group Policy.
Best Practices for Securing Local Administrator Password Group Policy in Server 2016
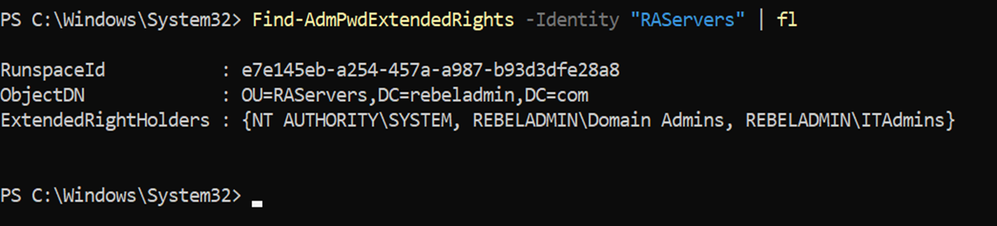
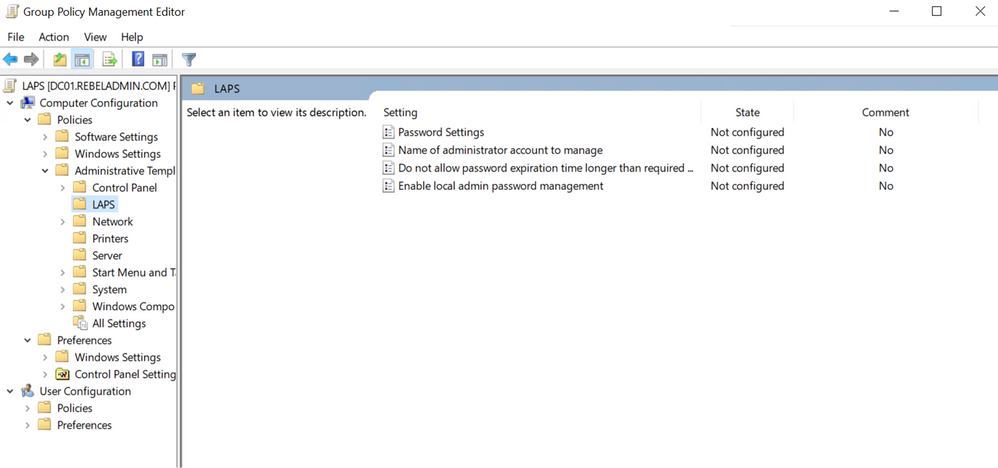
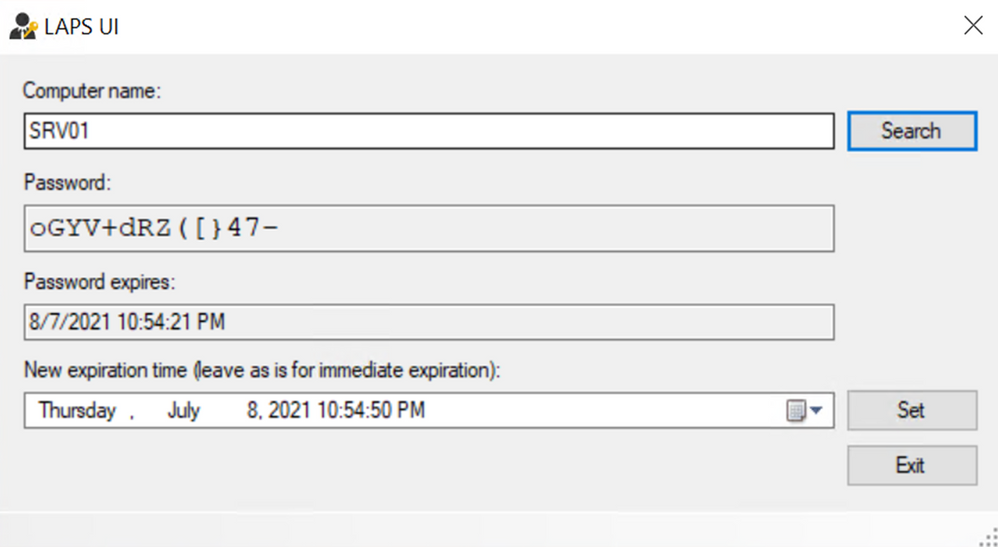
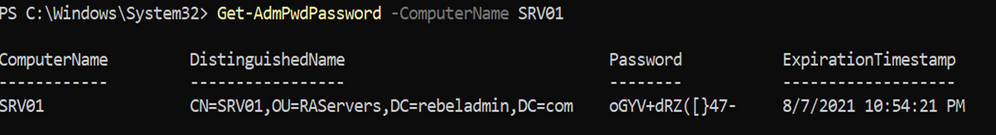
1. Implement the Local Administrator Password Solution (LAPS). LAPS is a Microsoft solution that provides a secure way to manage local administrator passwords on domain-joined computers. It stores the local administrator passwords in Active Directory (AD) and provides a secure way to manage them.
2. Use Group Policy to enforce password complexity and length. Group Policy can be used to enforce password complexity and length requirements for local administrator accounts. This will help ensure that the passwords are strong and difficult to guess.
3. Use Group Policy to enforce regular password changes. Group Policy can be used to enforce regular password changes for local administrator accounts. This will help ensure that the passwords are changed on a regular basis and are not left unchanged for long periods of time.
4. Use Group Policy to restrict access to local administrator accounts. Group Policy can be used to restrict access to local administrator accounts. This will help ensure that only authorized users are able to access the accounts.
5. Use Group Policy to audit local administrator accounts. Group Policy can be used to audit local administrator accounts. This will help ensure that any changes to the accounts are tracked and can be investigated if necessary.
6. Use Group Policy to disable local administrator accounts. Group Policy can be used to disable local administrator accounts. This will help ensure that the accounts are not used for malicious purposes.
7. Use Group Policy to enable two-factor authentication for local administrator accounts. Group Policy can be used to enable two-factor authentication for local administrator accounts. This will help ensure that the accounts are secure and only accessible by authorized users.
How to Automate Local Administrator Password Group Policy Changes in Server 2016
Automating local administrator password group policy changes in Server 2016 is a straightforward process that can be completed in a few simple steps. This article will provide a step-by-step guide to help you automate the process.
First, open the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) by typing “gpmc.msc” in the Run dialog box. Once the GPMC is open, navigate to the domain or OU where the policy needs to be applied.
Next, right-click on the domain or OU and select “Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here…” from the context menu. Give the GPO a name and click OK.
Now, right-click on the newly created GPO and select “Edit” from the context menu. This will open the Group Policy Management Editor.
Navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Security Options.
In the right-hand pane, double-click on “Accounts: Rename administrator account” and select “Enabled”. Enter the new name for the local administrator account in the “Rename administrator account” field.
Next, double-click on “Accounts: Rename guest account” and select “Enabled”. Enter the new name for the local guest account in the “Rename guest account” field.
Finally, double-click on “Accounts: Limit local account use of blank passwords to console logon only” and select “Enabled”. This will prevent users from using blank passwords to log on to the local computer.
Once all the settings have been configured, click OK and close the Group Policy Management Editor. The changes will take effect the next time the computer is restarted.
By following these steps, you can easily automate local administrator password group policy changes in Server 2016. This will help ensure that the local administrator and guest accounts are secure and that users are not able to log on to the local computer with blank passwords.
Step-by-Step Guide
- Open Group Policy Management Console (GPMC): Start by opening the GPMC by typing “gpmc.msc” in the Run dialog box. Navigate to the domain or OU where the local administrator password group policy is applied.
- Edit Policy: Right-click on the policy and select “Edit”. This opens the Group Policy Editor. Navigate to “Computer Configuration” > “Policies” > “Windows Settings” > “Security Settings” > “Local Policies” > “Security Options”.
- Configure Audit Settings: In the Security Options section, locate the “Audit: Force audit policy subcategory settings (Windows Vista or later) to override audit policy category settings” policy. Right-click and select “Properties”. Check the “Define these policy settings” checkbox. Then, select “Success” and “Failure” checkboxes under “Audit these attempts” section.
- Save Changes: Click “OK” to save the changes.
- Check Event Viewer: Finally, open Event Viewer by typing “eventvwr.msc” in the Run dialog box. Navigate to “Windows Logs” > “Security” section. Look for events with the ID 4648. These events indicate any successful or failed attempts to change the local administrator password group policy.
By following these steps, you can effectively audit local administrator password group policy changes in Server 2016, ensuring your server remains secure.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When dealing with Local Administrator Password Group Policy (LAPG) in Server 2016, you may encounter some common issues. Here’s how to troubleshoot them:
- Incorrect Password Settings: Ensure password settings are configured correctly and meet minimum requirements.
- Incorrect Group Policy Settings: Check if group policy settings are configured and applied correctly.
- Incorrect Security Settings: Verify security settings are configured and applied correctly.
- Incorrect Permissions: Make sure permissions are configured and applied correctly.
By addressing these common issues, you can ensure LAPG is properly configured, maintaining a secure server environment.
Leveraging LAPG for Improved Security
To enhance security in Server 2016, leveraging Local Administrator Password Group Policy (LAPG) is key. LAPG allows administrators to centrally manage local administrator passwords across all computers in an Active Directory domain, ensuring strong, unique passwords are regularly changed.
- Create GPO: Start by creating a Group Policy Object (GPO) and link it to the domain. Configure password settings within the GPO, including length, complexity, and expiration period.
- Apply GPO: Once linked to the domain, the GPO will be applied to all computers, automatically changing local administrator passwords to the specified settings.
- Reduce Administrative Burden: Centralized management of passwords reduces the need for manual changes on each computer, saving time and resources for administrators.
By leveraging LAPG, administrators can significantly improve security in Server 2016, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and streamlining password management tasks.
Ensuring the security of your server is paramount in today’s digital landscape. By auditing local administrator password group policy changes, troubleshooting common issues, and leveraging LAPG, you can fortify your server against potential threats and maintain a robust security posture.